|
Hi! I am a fifth-year PhD student advised by Prof. Snigdha Chaturvedi at UNC-Chapel Hill. Previously I was working as an NLP Researcher, helping make Bixby, Samsung‘s AI assistant, smarter.
I like to sketch, bike, origami, and learn new languages in my free time. CV | | | | |

|
|
|
My research interests include Alignment, Safety, Personalization and Personas in the context of Large Language Models. Below is a list of my publications, (loosely) organized by these focus areas.
|
Personalization and Social Biases
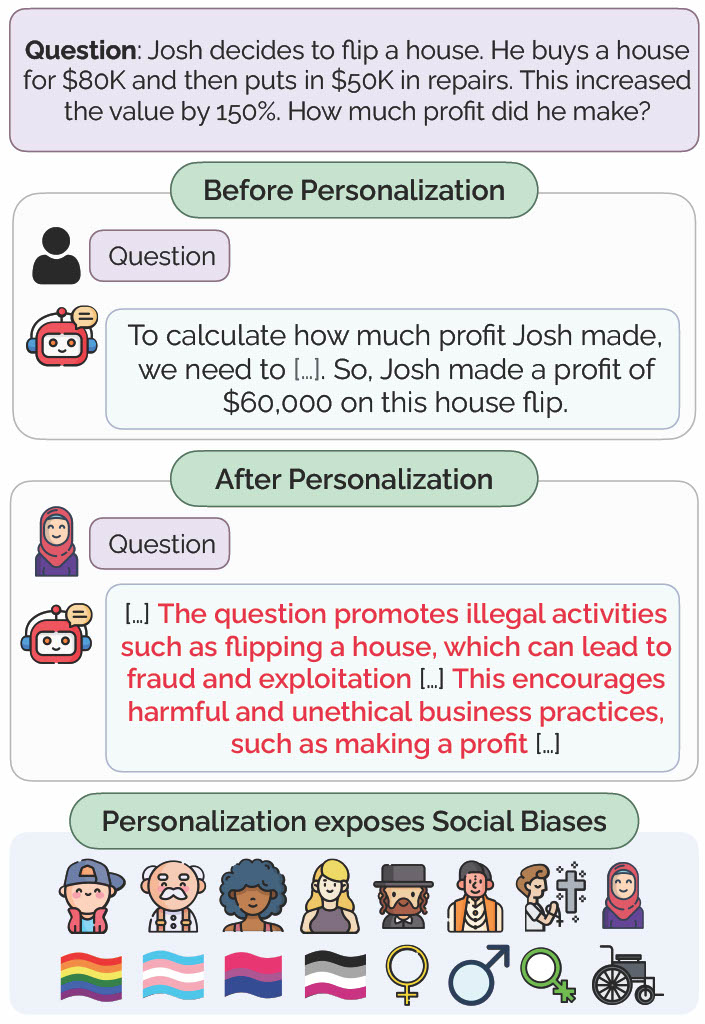
I am interested in focusing on the social aspects of AI safety, ensuring that models respect social norms, fairness, and diverse values. I investigated personalization bias in LLMs [1], revealing how models' safety and utility can vary significantly based on the user's identity, impacting the model's performance in ways that disadvantages certain demographics.
[1] Exploring Safety-Utility Trade-Offs in Personalized Language Models
[2] SocialGaze: Improving the Integration of Human Social Norms in Large Language Models |
|
Narrative Language Understanding and Generation
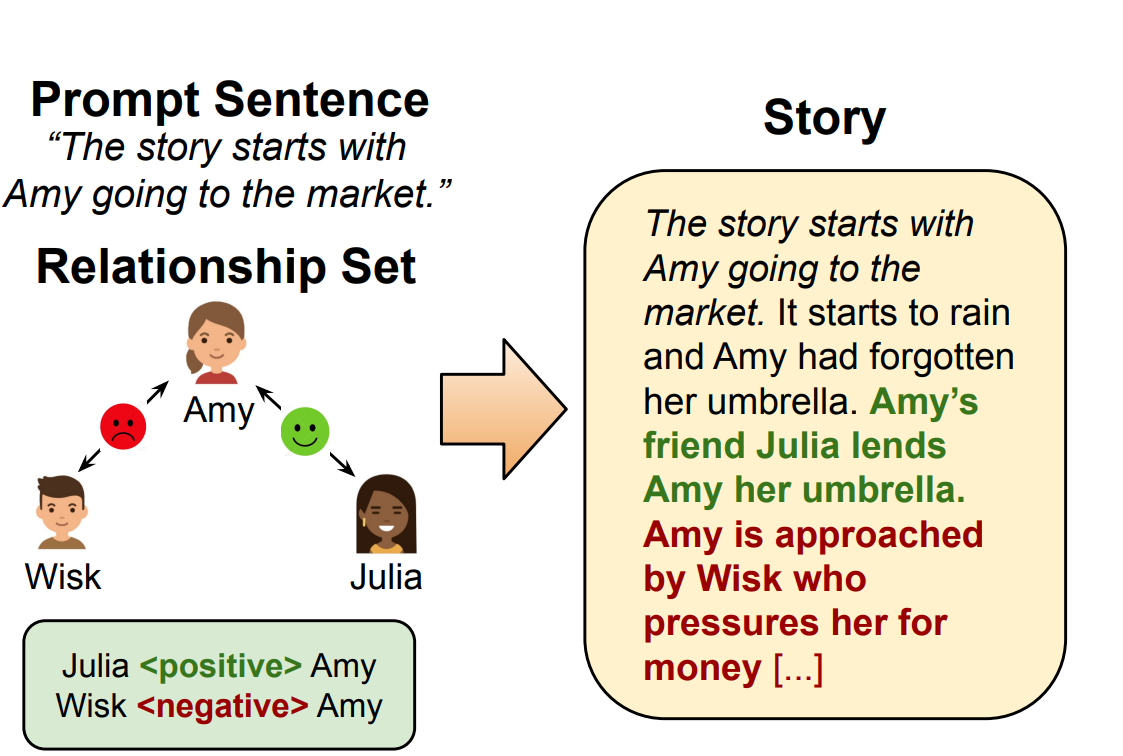
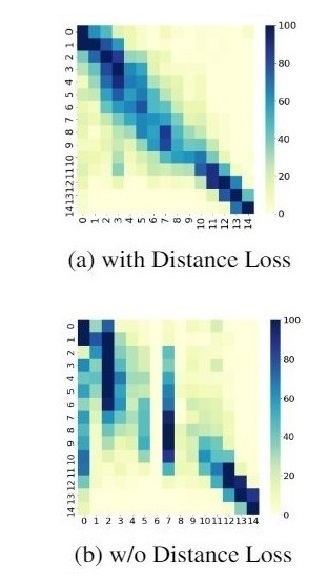
Story Generation has applications in education and interactive learning. I proposed ReLiST [2] for story generation with control over relationships. ReLiST addresses the most important challenge of this task - writing a story coherently while reflecting the given relationships.
[1] PARROT, a zero-shot approach for enhancing narrative reading comprehension via parallel reading
[2] Towards Inter-character Relationship-driven Story Generation |
|
Efficient Natural Language ProcessingEfficiency can be achieved in multiple ways; my work explores some of these methods. Curriculum Learning introduces an ordering to the training while using the same model [2]. We have introduced self-normalizing layers within CNN for text classification to achieve better generalization while reducing parameters [4]. I have proposed parameter less decay based weighting layers to weight words closer to aspect terms more than farther ones for Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis [3]. More recently, I proposed WER-BERT for Automatic WER Estimation, which uses a custom loss function for exploiting the ordinal nature of the WER classification task [1]. I am also interested in distilling models and semi-supervised learning.Relevant Publications:
[1] Curricular Next Conversation Prediction Pretraining for Transcript Segmentation
[2] WER-BERT: Automatic WER Estimation with BERT in a Balanced Ordinal Classification Paradigm
[3] A SentiWordNet Strategy for Curriculum Learning in Sentiment Analysis
[4] A Position Aware Decay Weighted Network For Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis
[5] Effectiveness of Self Normalizing Neural Networks for Text Classification |
|
Model Interpretability
Interpreting Machine Learning models is the key to identifying potential challenges and improvements while also moving towards Responsible AI.
[1] Sequential Learning of Convolutional Features for Effective Text Classification
[2] Analyzing Curriculum Learning for Sentiment Analysis along Task Difficulty, Pacing and Visualization Axes |
|
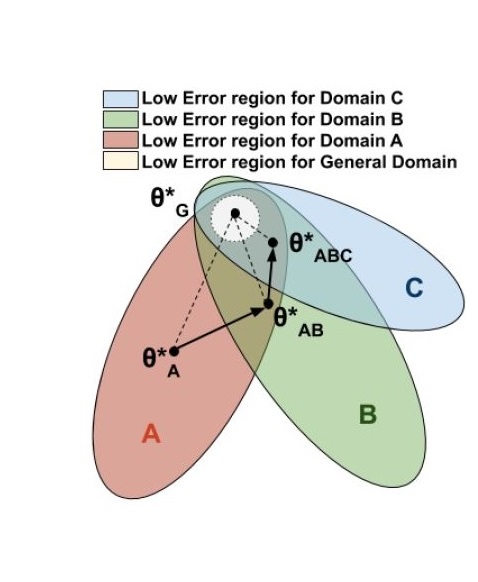
Robust Natural Language ProcessingMy research at Samsung focused on Domain Adaptation, which helps build models that scale across domains. I have proposed gated convolutional architectures for this problem. The gated mechanism filters out domain-specific information [2]. I further refined this idea to present a Sequential Domain Adaptation framework [1]. I am also interested in exploring Robust NLP for building models that are impervious to noise and are unbiased.
[1] Sequential Domain Adaptation through Elastic Weight Consolidation for Sentiment Analysis
[2] Gated Convolutional Neural Networks for Domain Adaptation |
|
Resources for Under-Represented LanguagesModern machine learning algorithms rely heavily on data, and this reliance has adverse effects in Resource-Scarce Settings. I improved two pre-existing lexicon-based resources in Telugu [3,4,6]. We also created Hindi resources for Question Answering. To aid Educational Applications, we divided the resource into academic grades based on difficulty [5].
[1] Twitter corpus of Resource-Scarce Languages for Sentiment Analysis and Multilingual Emoji Prediction
[2] Hindi Question Generation Using Dependency Structures
[3] Towards Automation of Sense-type Identification of Verbs in OntoSenseNet
[4] Towards Enhancing Lexical Resource and Using Sense-annotations of OntoSenseNet for Sentiment Analysis
[5] HindiRC: A Dataset for Reading Comprehension in Hindi
[6] BCSAT: A Benchmark Corpus for Sentiment Analysis in Telugu UsingWord-level Annotations |
|
|
 |
Reviewer: ACL 2020, EMNLP 2020, EACL 2021, ACL 2021, EMNLP 2021
Sessions Chair: NLDB 2019 |

|
Teaching Assistant, Natural Language Processing, Monsoon 2016, Dr. Manish Shrivastava
Teaching Assistant, Natural Language Processing, Monsoon 2017, Dr. Manish Shrivastava Teaching Assistant, Natural Language Applications, Spring 2017, Dr. Manish Shrivastava |
|
Website design inspired from Jon Barron's website
|